Healthcare Solutions
Delivering Superior Care & Patient Safety
At Northern Light, patients are at the center of everything we do. Our radiologists provide fast, accurate results, giving physicians the insights they need to deliver the highest quality of care. Through advanced technology, secure communication, and a commitment to excellence, we ensure every patient receives compassionate, reliable, and timely diagnostic support.
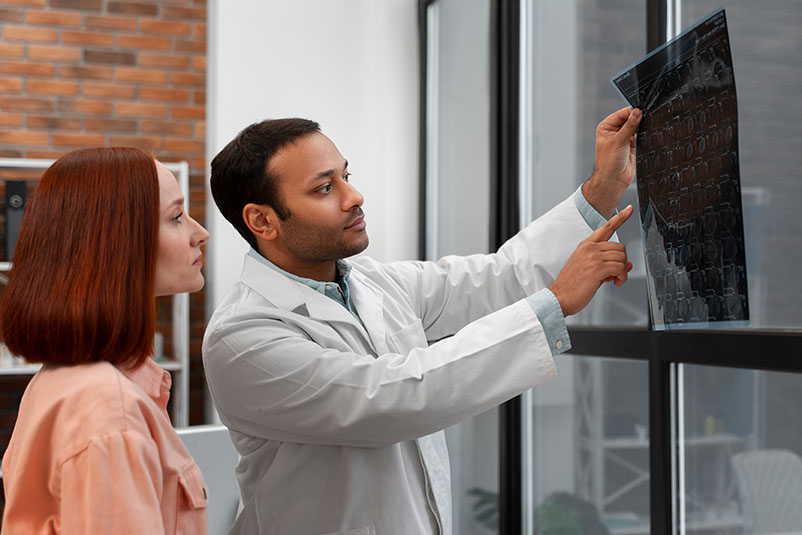


Radiologists are medical doctors who specialize in diagnosing and treating injuries and diseases using medical imaging (radiology) procedures (exams/tests) such as X-rays, computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), nuclear medicine, positron emission tomography (PET) and ultrasound.
Radiologists complete at least 13 years of training, including medical school, a four-year residency, and most often, an additional one- or two-year fellowship of very specialized training, such as radiation oncology, pediatric radiology, or interventional radiology. They are certified by the American Board of Radiology, and they have exacting requirements for continuing medical education throughout their practicing years.